Causes
Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive genetic disease, in which the shape of the haemoglobin protein of the red blood cell in the blood is altered. It is caused by inheritance of two sickle cells one from each parent.
Haemoglobin protein contains four protein subunits, two subunits called alpha-globin and two subunits called beta-globin. Many different beta-globins are produced from many different mutations in haemoglobin. Haemoglobin S for example is a mutation that results in abnormal beta-globin. Haemoglobin C or E can also produce more abnormal beta-globin subunits. Sickle cell suffereres have at least one of their beta-globin subunits replaced by an abnormal haemoglobin S or C.
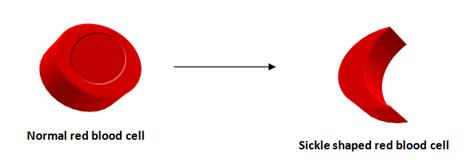
In a healthy individual red blood cell structure is round and concave, allowing blood to flow easily through the vessels. Abnormal beta-globin changes the structure of red blood cells in to a sickle shape, this reduces blood flow around the body, because the red blood cells get trapped in the blood vessels. This can damage tissue and organs, because blood flow has decreased and as a result, body organs do not receive sufficient nutrients and oxygen.
Below is a useful link, which shows a video clip of Sickle cell Anaemia patients
